PKCS11 » History » Revision 2
« Previous |
Revision 2/7
(diff)
| Next »
Johannes Schmölz, 12/19/2012 11:44 AM
PKCS11¶
The main goal of the PKCS#11-interface of the Open eCard App is to provide the functionality, which is required by Mozilla’s Firefox browser.
Mozilla’s overall crypto architecture as taken from [Grif09] is depicted in Figure 1.
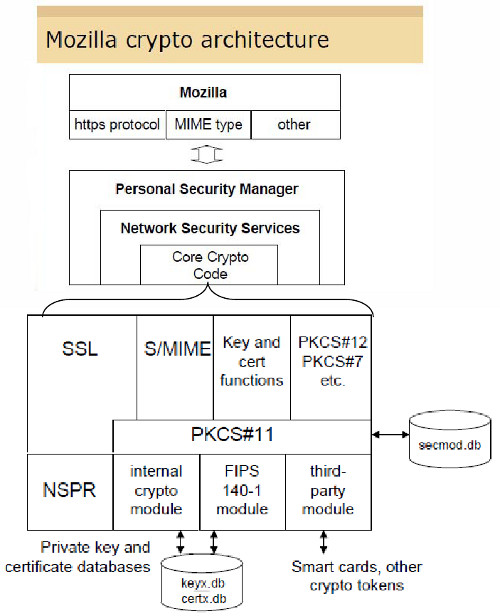
Figure 1: Mozilla's Cryptographic Architecture ([Grif09], p. 22)
The important part is the usage of the PKCS#11-interface by the “Core Crypto Code” within the “Network Security Services” as explained in [NSS-PKCS#11].
As this browser is a successor of Netscape’s Communicator it is expected that the PKCS#11-usage in today’s Firefox is similar to the PKCS#11-usage explained in [NSS-PKCS#11].
Required Functions¶
General-Purpose Functions¶
Among the general-purpose functions defined in Section 11.4 of [NSS-PKCS#11] the following functions need to be supported:
C_InitializeC_FinalizeC_GetFunctionListC_GetInfo
C_Initialize
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_Initialize on startup or when it loads a new module. The Netscape Security Library always passes NULL, as required by the PKCS #11 specification, in the single C_Initialize parameter pReserved. This function will use the IFD-function EstablishContext to initialize the IFD-module.
C_Finalize
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_Finalize on shutdown and whenever it unloads a module.
This function will use the IFD-function ReleaseContext to initialize the IFD-module.
C_GetInfo
The Netscape Security Library calls C_GetInfo on startup or when it loads a new module. The version numbers, manufacturer IDs, and so on are displayed when the user views the information. The supplied library names are used as the default library names; currently, these names should not include any double quotation marks.
This function will only return static information and does not involve any IFD-function.
C_GetFunctionList
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetFunctionList on startup or when it loads a new module. In [NSS-PKCS#11] it is recommended that for a not implemented function there should at least be a stub that returns CKR_FUNCTION_NOT_SUPPORTED.
This function will only return static information and does not involve any IFD-function.
Slot and Token Management¶
C_GetSlotList
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetSlotList on startup or when it loads a new module, requests all the module's slots, and keeps track of the list from that point on. The slots are expected to remain static: that is, the module never has more slots or fewer slots than the number on the original list. This means that the function C_WaitForSlotEvent is not used by the Netscape Security Library.
This function uses the following IFD-functions:
ListIFDsGetIFDCapabilitiesGetStatus
C_GetSlotInfo
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetSlotInfo on startup or when it loads a new module and reads in the information that can be viewed on the slot information page. If the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is set, the Netscape Security Library also calls C_GetSlotInfo whenever it looks up slots to make sure the token is present. If the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is not set, the Netscape Security Library uses that token information without checking again.
If the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is not set, the CKF_TOKEN_PRESENT flag must be set, or else the Netscape Security Library marks the slot as bad and will never use it.
The Netscape Security Library doesn't currently use the CKF_HW_SLOT flag.
For a particular slot this function returns the following structure:
typedef struct CK_SLOT_INFO {
CK_UTF8CHAR slotDescription[64];
CK_UTF8CHAR manufacturerID[32];
CK_FLAGS flags;
CK_VERSION hardwareVersion;
CK_VERSION firmwareVersion;
} CK_SLOT_INFO;
Listing 1:
CK_SLOT_INFO structure
C_GetTokenInfo
If a token is a permanent device (that is, if the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is not set), the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetTokenInfo only on startup or when it loads a new module. If the token is a removable device, the Netscape Security Library may call C_GetTokenInfo anytime it's looking for a new token to check whether the token is write protected, whether it can generate random numbers, and so on.
The Netscape Security Library expects CK_TOKEN_INFO label to contain the name of the token.
If the CKF_WRITE_PROTECTED flag is set, the Netscape Security Library won't use the token to generate keys.
The Netscape Security Library interprets the combination of the CKF_LOGIN_REQUIRED and CKF_USER_PIN_INITIALIZED flags as shown in the following table.
CFK_LOGIN_REQUIRED |
CFK_USER_PIN_INITIALIZED |
Netscape Security Library assumes that: |
|---|---|---|
FALSE |
FALSE |
This is a general access device. The Netscape Security Library will use it without prompting the user for a PIN. |
TRUE |
FALSE |
The device is uninitialized. The Netscape Security Library attempts to initialize the device only if it needs to generate a key or needs to set the user PIN. The Netscape Security Library calls C_InitPIN to initialize the device and set the user PIN; if these calls are successful, the key is generated and at that point the CFK_USER_PIN_INITIALIZED flag should change from FALSE to TRUE. |
FALSE |
TRUE |
This is a general access device that can have a PIN set on it. Because it's a general access device, the Netscape Security Library never prompts for the PIN, even though it's possible to set a PIN with C_SetPIN. If the PIN is set successfully, the CFK_LOGIN_REQUIRED flag should change to TRUE. The Netscape Security Library uses this combination of flags for its internal token when the key database password is NULL. These are not standard PKCS #11 semantics; they are intended for the Netscape Security Library's internal use only. |
TRUE |
TRUE |
The device has been initialized and requires authentication. The Netscape Security Library checks whether the user is logged on, and if not prompts the user for a PIN. |
Table 1: Interpretation of flags ([NSS-PKCS#11], Table 1.1)
For a typical signature card in operational mode the two flags are TRUE. On the other side the two flags for the private key on the eGK, which is used for card2card-authentication, are both FALSE.
This function returns the CK_TOKEN_INFO struct for a specific token.
typedef struct CK_TOKEN_INFO {
CK_UTF8CHAR label[32];
CK_UTF8CHAR manufacturerID[32];
CK_UTF8CHAR model[16];
CK_CHAR serialNumber[16];
CK_FLAGS flags;
CK_ULONG ulMaxSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulMaxRwSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulRwSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulMaxPinLen;
CK_ULONG ulMinPinLen;
CK_ULONG ulTotalPublicMemory;
CK_ULONG ulFreePublicMemory;
CK_ULONG ulTotalPrivateMemory;
CK_ULONG ulFreePrivateMemory;
CK_VERSION hardwareVersion;
CK_VERSION firmwareVersion;
CK_CHAR utcTime[16];
} CK_TOKEN_INFO;
Listing 2:
CK_TOKEN_INFO structure ([PKCS#11(v2.3)], p. 37)
C_GetMechanismList
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11], the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetMechanismList fairly frequently to identify the mechanisms supported by a token.
This function returns the CK_MECHANISM_INFO struct for a specific token.
typedef struct CK_MECHANISM_INFO {
CK_ULONG ulMinKeySize;
CK_ULONG ulMaxKeySize;
CK_FLAGS flags;
} CK_MECHANISM_INFO;
Listing 3:
CK_MECHANISM_INFO structure ([PKCS#11(v2.3)], p. 49)
| Bit Flag | Mask | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
CKF_HW |
0x00000001 | True if the mechanism is performed by the device; false if the mechanism is performed in software |
CKF_ENCRYPT |
0x00000100 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_EncryptInit |
CKF_DECRYPT |
0x00000200 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_DecryptInit |
CKF_DIGEST |
0x00000400 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_DigestInit |
CKF_SIGN |
0x00000800 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_SignInit |
CKF_SIGN_RECOVER |
0x00001000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_SignRecoverInit |
CKF_VERIFY |
0x00002000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_VerifyInit |
CKF_VERIFY_RECOVER |
0x00004000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_VerifyRecoverInit |
CKF_GENERATE |
0x00008000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_GenerateKey |
CKF_GENERATE_KEY_PAIR |
0x00010000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_GenerateKeyPair |
CKF_WRAP |
0x00020000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_WrapKey |
CKF_UNWRAP |
0x00040000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_UnwrapKey |
CKF_DERIVE |
0x00080000 | True if the mechanism can be used with C_DeriveKey |
CKF_EXTENSION |
0x80000000 | True if there is an extension to the flags; false if no extensions. Must be false for this version. |
Table 2: Mechanism Information Flags ([PKCS#11(v2.3)], p. 50)
Session Management¶
C_OpenSession
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_OpenSession whenever it initializes a token and keeps the session open as long as possible. The Netscape Security Library almost never closes a session after it finishes doing something with a token. It uses a single session for all single-part RSA operations such as logging in, logging out, signing, verifying, generating keys, wrapping keys, and so on.
The Netscape Security Library opens a separate session for each part of a multipart encryption (bulk encryption). If it runs out of sessions, it uses the initial session for saves and restores.
This function will use the IFD-function Connect to open a session to the token.
C_CloseSession
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_CloseSession to close sessions created for bulk encryption.
This function will use the IFD-function Disconnect to close a session to the token.
C_CloseAllSessions
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library may call C_CloseAllSessions when it closes down a slot.
C_GetSessionInfo
The Netscape Security Library calls C_GetSessionInfo frequently.
If a token has been removed during a session, C_GetSessionInfo should return either CKR_SESSION_CLOSED or CKR_SESSION_HANDLE_INVALID. If a token has been removed and then the same or another token is inserted, C_GetSessionInfo should return CKR_SESSION_HANDLE_INVALID.
C_Login
The Netscape Security Library calls C_Login on a token's initial session whenever CKF_LOGIN_REQUIRED is TRUE and the user state indicates that the user isn't logged in.
This function will use the IFD-function VerifyUser to perform the authentication of a user.
C_Logout
The Netscape Security Library calls C_Logout on a token's initial session
- when the password is timed out
- when performing any kind of private key operation if "ask always" is turned on
- when changing a password
- when the user logs out
Object Management¶
In the scope of a TLS-handshake the client needs to read the certificate from the card and send it to the server. This functionality is most likely performed using the following two functions.
C_GetAttributeValue
The Netscape Security Library calls C_GetAttributeValue to get the value of attributes for both single objects and multiple objects. This is useful for extracting public keys, nonsecret bulk keys, and so on.
C_FindObjectsInit, C_FindObjects, C_FindFinal
The Netscape Security Library calls these functions frequently to look up objects by CKA_ID or CKA_LABEL. These values must match the equivalent values for related keys and certificates and must be unique among key pairs on a given token.
The Netscape Security Library also looks up certificates by CK_ISSUER and CK_SERIAL. If those fields aren't set on the token, S/MIME won't work.
Cryptographic Operations¶
In the scope of a TLS-handshake the client needs to sign data, which is constructed based on previously exchanged messages in the handshake. This signature is most likely created using the functions C_SignInit, C_Sign and C_SignFinal.
References¶
[Grif09] R. Griffin: Encryption and Key Management Tutorials, Part II: PKCS #11 – Enhancements and Opportunities, Talk at RSA 2009, ftp://ftp.rsasecurity.com/pub/pkcs/pkcs-11/v2-30/TUT-M51_Griffin_PKCS11.pdf
[NSS-PKCS#11] Implementing PKCS #11 for the Netscape Security Library, http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19957-01/816-6150-10/pkcs.htm
[PKCS#11(v2.3)] RSA Laboratories: PKCS #11 Base Functionality v2.30: Cryptoki – Draft 4, 10 July 2009
Updated by Johannes Schmölz about 13 years ago · 2 revisions