PKCS11 » History » Revision 1
Revision 1/7
| Next »
Johannes Schmölz, 12/18/2012 07:43 PM
PKCS11¶
The main goal of the PKCS#11-interface of the Open eCard App is to provide the functionality, which is required by Mozilla’s Firefox browser.
Mozilla’s overall crypto architecture as taken from [Grif09] is depicted in Figure 1.
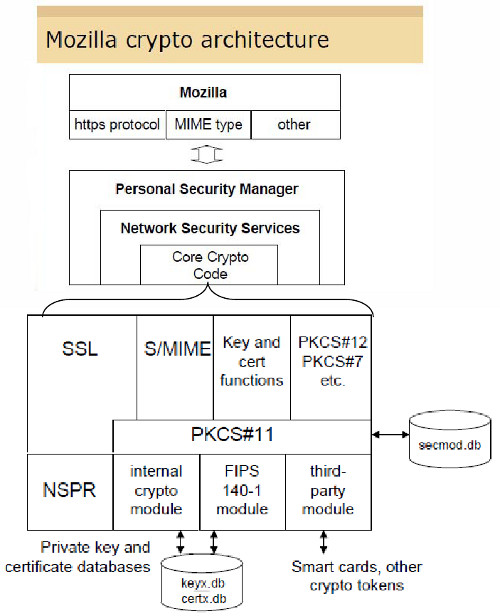
Figure 1: Mozilla's Cryptographic Architecture
The important part is the usage of the PKCS#11-interface by the “Core Crypto Code” within the “Network Security Services” as explained in [NSS-PKCS#11].
As this browser is a successor of Netscape’s Communicator it is expected that the PKCS#11-usage in today’s Firefox is similar to the PKCS#11-usage explained in [NSS-PKCS#11].
Required Functions¶
General-Purpose Functions¶
Among the general-purpose functions defined in Section 11.4 of [NSS-PKCS#11] the following functions need to be supported:
- C_Initialize
- C_Finalize
- C_GetFunctionList
- C_GetInfo
C_Initialize
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_Initialize on startup or when it loads a new module. The Netscape Security Library always passes NULL, as required by the PKCS #11 specification, in the single C_Initialize parameter pReserved. This function will use the IFD-function EstablishContext to initialize the IFD-module.
C_Finalize
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_Finalize on shutdown and whenever it unloads a module.
This function will use the IFD-function ReleaseContext to initialize the IFD-module.
C_GetInfo
The Netscape Security Library calls C_GetInfo on startup or when it loads a new module. The version numbers, manufacturer IDs, and so on are displayed when the user views the information. The supplied library names are used as the default library names; currently, these names should not include any double quotation marks.
This function will only return static information and does not involve any IFD-function.
C_GetFunctionList
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetFunctionList on startup or when it loads a new module. In [NSS-PKCS#11] it is recommended that for a not implemented function there should at least be a stub that returns CKR_FUNCTION_NOT_SUPPORTED.
This function will only return static information and does not involve any IFD-function.
Slot and Token Management¶
C_GetSlotList
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetSlotList on startup or when it loads a new module, requests all the module's slots, and keeps track of the list from that point on. The slots are expected to remain static: that is, the module never has more slots or fewer slots than the number on the original list. This means that the function C_WaitForSlotEvent is not used by the Netscape Se-curity Library.
This function uses the following IFD-functions:
- ListIFDs
- GetIFDCapabilities
- GetStatus
C_GetSlotInfo
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetSlotInfo on startup or when it loads a new module and reads in the information that can be viewed on the slot information page. If the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is set, the Netscape Security Library also calls C_GetSlotInfo whenever it looks up slots to make sure the token is present. If the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is not set, the Netscape Security Library uses that token information without checking again.
If the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is not set, the CKF_TOKEN_PRESENT flag must be set, or else the Netscape Security Library marks the slot as bad and will never use it.
The Netscape Security Library doesn't currently use the CKF_HW_SLOT flag.
For a particular slot this function returns the following structure:
typedef struct CK_SLOT_INFO {
CK_UTF8CHAR slotDescription[64];
CK_UTF8CHAR manufacturerID[32];
CK_FLAGS flags;
CK_VERSION hardwareVersion;
CK_VERSION firmwareVersion;
} CK_SLOT_INFO;
C_GetTokenInfo
If a token is a permanent device (that is, if the CKF_REMOVABLE_DEVICE flag is not set), the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetTokenInfo only on startup or when it loads a new module. If the token is a removable device, the Netscape Security Library may call C_GetTokenInfo anytime it's looking for a new token to check whether the token is write protected, whether it can generate random numbers, and so on.
The Netscape Security Library expects CK_TOKEN_INFO.label to contain the name of the token.
If the CKF_WRITE_PROTECTED flag is set, the Netscape Security Library won't use the token to generate keys.
The Netscape Security Library interprets the combination of the CKF_LOGIN_REQUIRED and CKF_USER_PIN_INITIALIZED flags as shown in the following table.
TODO: insert table
For a typical signature card in operational mode the two flags are TRUE. On the other side the two flags for the private key on the eGK, which is used for card2card-authentication, are both FALSE.
This function returns the CK_TOKEN_INFO struct for a specific token.
typedef struct CK_TOKEN_INFO {
CK_UTF8CHAR label[32];
CK_UTF8CHAR manufacturerID[32];
CK_UTF8CHAR model[16];
CK_CHAR serialNumber[16];
CK_FLAGS flags;
CK_ULONG ulMaxSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulMaxRwSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulRwSessionCount;
CK_ULONG ulMaxPinLen;
CK_ULONG ulMinPinLen;
CK_ULONG ulTotalPublicMemory;
CK_ULONG ulFreePublicMemory;
CK_ULONG ulTotalPrivateMemory;
CK_ULONG ulFreePrivateMemory;
CK_VERSION hardwareVersion;
CK_VERSION firmwareVersion;
CK_CHAR utcTime[16];
} CK_TOKEN_INFO;
C_GetMechanismList
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11], the Netscape Security Library calls C_GetMechanismList fairly frequently to identify the mechanisms supported by a token.
This function returns the CK_MECHANISM_INFO struct for a specific token.
typedef struct CK_MECHANISM_INFO {
CK_ULONG ulMinKeySize;
CK_ULONG ulMaxKeySize;
CK_FLAGS flags;
} CK_MECHANISM_INFO;
TODO: insert table
Session Management¶
C_OpenSession
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_OpenSession whenever it initializes a token and keeps the session open as long as possible. The Netscape Security Library almost never closes a session after it finishes doing some-thing with a token. It uses a single session for all single-part RSA operations such as logging in, logging out, signing, verifying, generating keys, wrapping keys, and so on.
The Netscape Security Library opens a separate session for each part of a multipart encryption (bulk encryption). If it runs out of sessions, it uses the initial session for saves and restores.
This function will use the IFD-function Connect to open a session to the token.
C_CloseSession
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library calls C_CloseSession to close sessions created for bulk encryption.
This function will use the IFD-function Disconnect to close a session to the token.
C_CloseAllSessions
As explained in [NSS-PKCS#11] the Netscape Security Library may call C_CloseAllSessions when it closes down a slot.
C_GetSessionInfo
The Netscape Security Library calls C_GetSessionInfo frequently.
If a token has been removed during a session, C_GetSessionInfo should return either CKR_SESSION_CLOSED or CKR_SESSION_HANDLE_INVALID. If a token has been removed and then the same or another token is inserted, C_GetSessionInfo should return CKR_SESSION_HANDLE_INVALID.
C_Login
The Netscape Security Library calls C_Login on a token's initial session whenever CKF_LOGIN_REQUIRED is TRUE and the user state indicates that the user isn't logged in.
This function will use the IFD-function VerifyUser to perform the authentication of a user.
C_Logout
The Netscape Security Library calls C_Logout on a token's initial session
- when the password is timed out
- when performing any kind of private key operation if "ask always" is turned on
- when changing a password
- when the user logs out
Object Management¶
In the scope of a TLS-handshake the client needs to read the certificate from the card and send it to the server. This functionality is most likely performed using the following two functions.
C_GetAttributeValue
The Netscape Security Library calls C_GetAttributeValue to get the value of attrib-utes for both single objects and multiple objects. This is useful for extracting public keys, nonsecret bulk keys, and so on.
C_FindObjectsInit, C_FindObjects, C_FindFinal
The Netscape Security Library calls these functions frequently to look up objects by CKA_ID or CKA_LABEL. These values must match the equivalent values for related keys and certificates and must be unique among key pairs on a given token.
The Netscape Security Library also looks up certificates by CK_ISSUER and CK_SERIAL. If those fields aren't set on the token, S/MIME won't work.
Cryptographic Operations¶
In the scope of a TLS-handshake the client needs to sign data, which is constructed based on previously exchanged messages in the handshake. This signature is most likely created using the functions C_SignInit, C_Sign and C_SignFinal.
References¶
[Grif09] R. Griffin: Encryption and Key Management Tutorials, Part II: PKCS #11 – Enhancements and Opportunities, Talk at RSA 2009, ftp://ftp.rsasecurity.com/pub/pkcs/pkcs-11/v2-30/TUT-M51_Griffin_PKCS11.pdf
[NSS-PKCS#11] Implementing PKCS #11 for the Netscape Security Library, http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E19957-01/816-6150-10/pkcs.htm
Updated by Johannes Schmölz about 13 years ago · 1 revisions